
When traveling or living abroad, you might hear about embassies and consulates. While both play essential roles in representing a country overseas, they serve different functions. Understanding the difference between a consulate and an embassy can help you know where to go when you need assistance abroad.
What Is an Embassy?
An embassy is the highest diplomatic representation of one country in another. It serves as the official communication channel between the governments of the two nations. Embassies are always located in the host country’s capital city. For example, the U.S. Embassy in Japan is located in Tokyo, while the British Embassy in the United States is in Washington, D.C.
The embassy’s primary role is to maintain diplomatic and political relations between the two countries. It helps develop policies, negotiate treaties, and monitor political developments in the host nation.
The head of an embassy is the ambassador. An ambassador is the highest-ranking official representing their country of origin. Ambassadors meet with key political leaders, attend official events, and work on building international partnerships.
Key Roles of an Embassy
– Diplomatic Communication: Embassies manage formal contact between governments.
– Political Negotiations: They engage in dialogue about trade agreements, defense pacts, and global cooperation.
– Crisis Management: Embassies help in cases of political turmoil, war, or evacuation.
– Economic Relations: They support businesses from their home country and foster economic ties.
– Defense and Intelligence: Embassies also work with intelligence and military liaisons.
Embassies play a crucial role in shaping a nation’s foreign policy. They act as the eyes and ears of their home government in a foreign land.
What Is a Consulate?
A consulate is a smaller, local branch of an embassy. While embassies handle political and diplomatic work, consulates focus on assisting citizens and managing administrative tasks. Consulates are found in major cities outside the capital.
For instance, in Germany, the U.S. Embassy is in Berlin, but there are U.S. consulates in Frankfurt, Munich, and Hamburg.
The head of a consulate is known as a consul or consul general (for larger consulates). Their role is to protect the interests of their home country’s citizens, especially travelers and expatriates.
Main Services Offered by Consulates
– Visa Services: They issue travel, work, and student visas to people visiting the consul’s home country.
– Passport Renewals: Citizens can renew passports and update official documents.
– Emergency Assistance: If a citizen is injured, arrested, or dies abroad, the consulate helps manage the situation.
– Notarization and Legal Support: Consulates provide legal certifications and document validation.
– Travel Advisory: They offer guidance about local laws, safety, and travel restrictions.
Consulates don’t get involved in political matters. Their job is to assist individuals and businesses with day-to-day administrative services.
Where Are They Located?
Embassies are found only in capital cities. This is because most government institutions and international negotiations take place in the capital. For instance:
– U.S. Embassy in Mexico is in Mexico City
– Indian Embassy in the UK is in London
Consulates, on the other hand, are located in major cities where there is a need for citizen services or a high volume of travelers. These cities could include:
– Barcelona, Milan, Shanghai, or Sydney
– They serve areas with large foreign populations or business centers

Embassy vs Consulate: The Organizational Hierarchy
Embassies and consulates are part of a country’s diplomatic mission abroad. Embassies are the central body, while consulates are sub-units that report to the embassy.
For example, if there’s a serious issue, such as a natural disaster or political upheaval, consulates report it to the embassy. The embassy then coordinates with the home government for action.
Embassies oversee the operations of all consulates in the country. They ensure every office is operating within the diplomatic framework.
When Should You Visit a Consulate Instead of an Embassy?
If you’re abroad and need help, you may wonder which office to visit. Here’s a simple rule:
– Visit the embassy if your issue is political, diplomatic, or involves high-level government affairs.
– Go to the consulate if your problem is personal, legal, or administrative.
Examples of Consulate Services:
– You lost your passport while traveling.
– You were arrested or need legal representation.
– You require a visa for your foreign friend.
– You need a birth certificate or notarized document.
Examples of Embassy Services:
– You’re part of a business delegation or government official.
– You need support during war or political conflict.
– You require assistance with diplomatic immunity or asylum.

What Happens During a National Emergency?
During a national emergency such as a civil war or pandemic, both embassies and consulates may operate differently. In such cases:
– Embassies coordinate with the foreign ministry for large-scale evacuations.
– Consulates assist individuals on the ground with exit documents and travel planning.
For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic, consulates helped stranded tourists return home. Embassies worked with governments to arrange repatriation flights.
Consular Sections Within Embassies
Sometimes, an embassy may have a consular section inside the same building. This section performs consulate-like services such as:
– Issuing visas
– Renewing passports
– Assisting with emergencies
So, if there is no separate consulate in the city you’re in, the embassy’s consular section can assist you.
How They Work Together
Embassies and consulates don’t work in isolation. They form a cohesive network to protect and serve their citizens abroad. Here’s how they collaborate:
Daily Reporting: Consulates inform embassies about local developments and citizen issues.
Event Planning: They coordinate official visits and ceremonies.
Crisis Response: Both work together during disasters or security threats.
Data Sharing: Embassies provide policy updates that consulates share with the public.
This teamwork ensures consistent support across all regions in the host country.
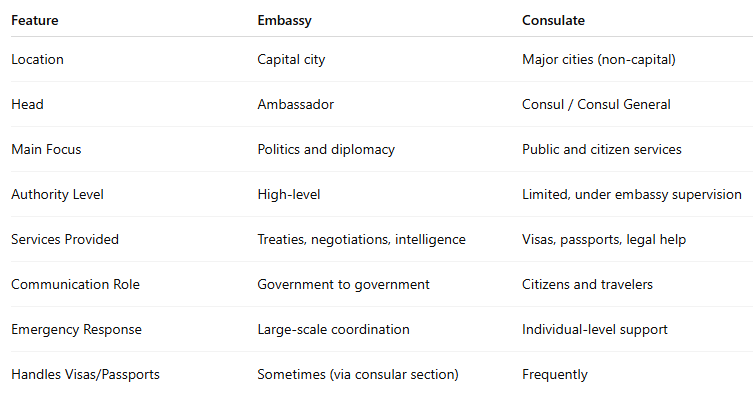
Embassy vs Consulate: Quick Comparison Table
FAQs
1. What is the main difference between a consulate and an embassy?
An embassy handles political and diplomatic relations, while a consulate deals with administrative services and citizen support.
2. Can I get a visa from an embassy?
Usually, visas are issued by consulates, not embassies, unless in rare cases or capital-only presence.
3. Are consulates open 24/7?
No, but they may offer emergency services after hours.
4. Do all countries have both embassies and consulates?
Not always. Smaller countries may only maintain embassies due to limited resources.
5. Can consulates help if I lose my passport abroad?
Yes, they are the primary place to go for lost or stolen passport issues.
6. What is an honorary consul?
An honorary consul is a local individual appointed to represent a foreign government in cities without a full consulate.
Conclusion
Embassies and consulates are two pillars of international relations. While they operate differently, they share the same goal—protecting and supporting their nation’s interests and citizens abroad.
An embassy is the command center for political and diplomatic activity. A consulate is the go-to place for travelers, students, workers, and residents needing help in everyday matters.
Whether you’re on vacation, studying abroad, or working overseas, knowing the difference between a consulate and an embassy can save you time and stress. Always keep the contact details of both nearby—because when you need help, the right office can make all the difference.

